HSRP notes. Theory.
Short HSRP tips:
- On a particular LAN, multiple hot standby groups may coexist and overlap.
- Each standby group emulates a single virtual router.
- For each standby group, a single well-known MAC address is allocated to the group, as well as an IP address. The IP address SHOULD belong to the primary subnet in use on the LAN, but MUST differ from the addresses allocated as interface addresses on all routers and hosts on the LAN, including virtual IP addresses assigned to other HSRP groups.
- HSRP router roles are Active and Standby
- HSRP runs on top of UDP and uses port 1985
- HSRP packets are sent to multicast address 224.0.0.2 with TTL 1
- Routers uses their own IP addresses as the source for protocol packets
- The router with a higher priority wins in active-standby election. If priorities are equal then higher IP address wins.
- Every standby router learns hello and holdtime values set in the hello message from Active router.
- Router uses virtual mac address as a source address of the sent HELLO messages ONLY when it is in the ACTIVE state
From Cisco.com :Table-1 Default HSRP Configuration
HSRP conventions:
Active Router - forwarding packets for the virtual router
Standby Router - the primary backup router
Standby Group - the set of routers participating in HSRP
Hello Time - the interval between HSRP hellos
Hold Time - th interval between the receipt of hellos
Pic.1 HSRP packet format:
Version: usually version value "0" means version 1 (RFC 2281). In version 2 --> there is a 4096 possible HSRP groups and another frame format.
Op Code: describes the type of message: (1 octet)
- "0" hello ---> router is participating in HSRP and enabled to become Active or standby
Pic.2 Router sends HSRR hello once in a hellotime period
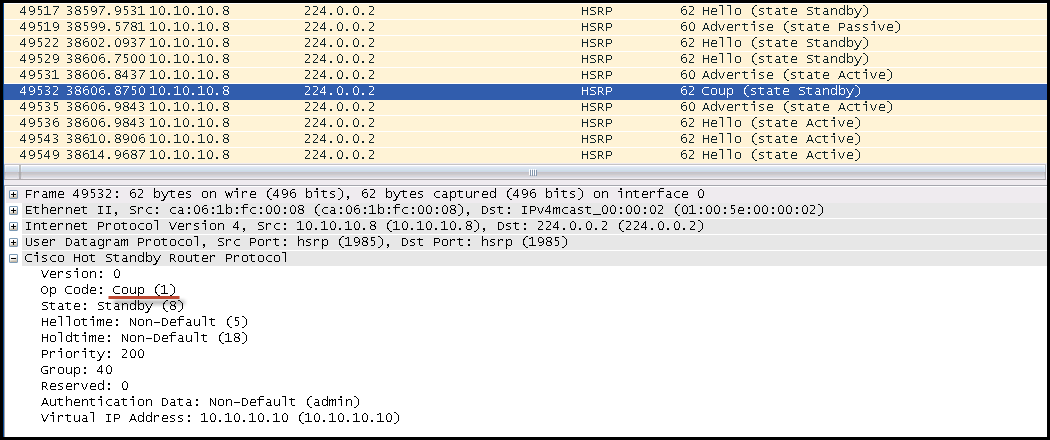
- "1" Coup ---> Router wishes to become the active router
Pic.3 HSRP router sends "Coup" message after changing priority to 200 and enabling Preempt feature:
- "2" Resign ---> router no longer wishes to be the active router
Pic.4 HSRP Resign message sent when "no standby 40 IP" command was entered:
- "3" Advertise ----> (not in RFC) Router that neither Active nor standby periodically send advertisements
Pic 5. HSRP Advertise message:
HSRP as a state machine:
Each HSRP router is implements a state of the HSRP state machine. Possible values are:
0 - Initial => starting state, HSRP is not running.
1 - Learn => router doesn't knows the virtual IP,it is waiting to hear hello messages from the active router
2 - Listen => router knows the virtual IP, but is neither active router nor standby, is listening hellos from all routers in a domain
4 - Speak => router sends periodic hellos and actively participate in election of active/standby router
8 - Standby => the router is a candidate to become the next active router, sends periodic hellos
16 - Active => the router is forwarding packets thet are sent to the group's virtual IP, send periodic hello messages
HSRP packet fields:
Hellotime - is given in seconds. ( 1 octet)
Holdtime - ( 1 octet) can be set manually in Cisco ( by RFC holdtime allowed to be learned from active router with authentication)
Priority - ( 1 octet) this field used to elect the active and standby router
Group - ( 1 octet) with a"Reserved" field there can be up to 4096 groups in Cisco HSRP
Authentication Data - (8 Octets)
Virtual IP address - (4 octets) The virtual IP address used by this group
Timers
Active_timer - monitors the activity of Active router. Starts when the hello message received from the Active router. Expires in the Holdtime after receiving Hello message
Standby_timer - monitors the activity of Standby router. Starts when the hello message received from the Standby router.
Hello_timer - expires in a hellotime period.
HSRP Preemption
Preemption should be enabled on the interface which priority allows to become the new active HSRP router. New appeared router with higher priority in HSRP group will become the new active router only if it will be enabled with preempt function.
Simple HSRP configuration
Interface IP address configuration:
R8(config)#int gi 0/0
R8(config-if)# ip address 10.10.10.8 255.255.255.0
Configure virtual IP for group 40:
R8(config-if)#standby 40 ip 10.10.10.10Setting priority
R8(config-if)#standby 40 priority 200Setting authentication with a plain text "admin"
R8(config-if)#standby 40 authentication text adminEnable preemption
R8(config-if)#standby 40 preemptConfigure tracking depended on interface loopback8 line state
R8(config-if)#standby 40 track loopback 8 ?<1-255> Decrement value
<cr>
R8(config-if)#standby 40 track loopback 8 70
R8(config-if)#standby 40 timers ?
<1-254> Hello interval in seconds
msec Specify hello interval in milliseconds
Change default HSRP timers values on the active router
R8(config-if)#standby 40 timers 4 ?<5-255> Hold time in seconds
R8(config-if)#standby 40 timers 4 15
Manually assign HSRP virtual MAC address
R8(config-if)#standby 40 mac-address ?H.H.H MAC address
R8(config-if)#standby 40 mac-address 0008.0008.0008 ?
<cr>
R8(config-if)#standby 40 mac-address 0008.0008.0008
Verify HSRP
R8(config-if)#do sh standGigabitEthernet0/0 - Group 40
State is Active
14 state changes, last state change 00:02:06
Virtual IP address is 10.10.10.10
Active virtual MAC address is 0008.0008.0008
Local virtual MAC address is 0008.0008.0008 (cfgd)
Hello time 4 sec, hold time 15 sec
Next hello sent in 1.328 secs
Authentication text, string "admin"
Preemption enabled
Active router is local
Standby router is 10.10.10.4, priority 140 (expires in 16.208 sec)
Priority 200 (configured 200)
Track interface Loopback8 state Up decrement 70
Group name is "hsrp-Gi0/0-40" (default)
Q&A
Q: How do HSRP version 1 and 2 inter operate?
A: HSRP Version 2 and 1 can not inter operate.
Q: what are HSRP roles?
A: Active and Standby.
Q: What is a HSRP packet's destination IP address and TTL? for 1 and 2 version of HSRP protocol.
A: HSRP V1 224.0.0.2 TTL 1 and HSRP V2 224.0.0.102 TTL 1
Q: What protocol HSRP uses as a transport
A: UDP port 1985
Q: What address uses router as a source address for HSRP protocol packets?
A: Routers uses their own interface IP addresses.
Q: What router will win HSRP master election? what is a tie breaking?
A: router with a numerically higher priority value will win, tie breaking is a IP address: higher IP address will win.
Q: How to create up to 4096 HSRP groups? Is it possible?
A: Yes. to create up to 4096 HSRP groups you must enable version 2 of HSRP protocol
Q: How to enable preemption between hsrp routers?
A: You should enable preemption on the router that can become an active HSRP router in case the current active router fails.
Q: What is the virtual mac address for the HSRP group number?
A: 0000.0C07.ACxx where xx is the number of HSRP group in HEX
Q: Does HSRP router uses virtual mac address as the source interface of HSRP hello messages? when?
A: HSRP router uses virtual mac address as source address in the HSRP hello message only when this router is in the active state.
Best regards!
Kravets Dmitry.




No comments:
Post a Comment